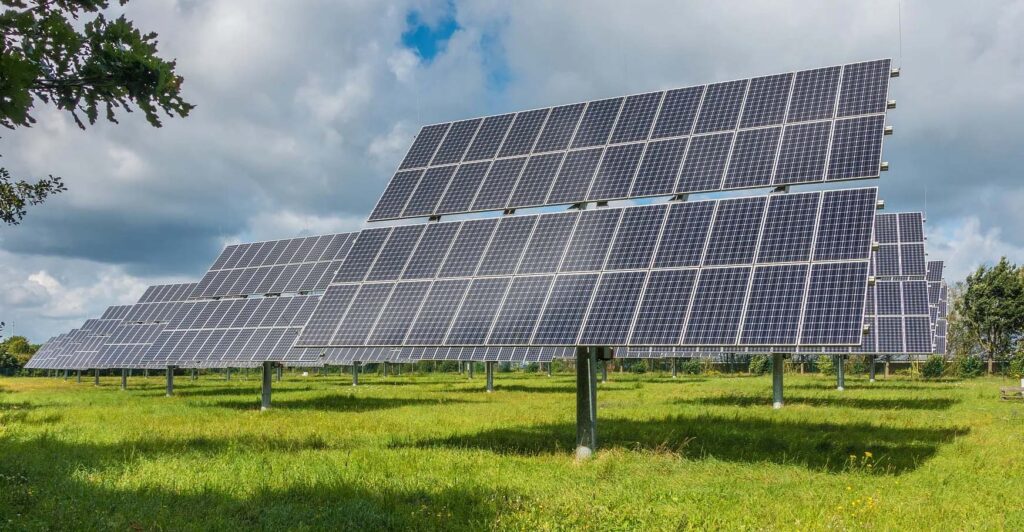
Solar panels are a key component of eco-homes, harnessing sunlight to generate electricity. They offer a sustainable and renewable energy source that can significantly reduce energy bills and the home’s carbon footprint.
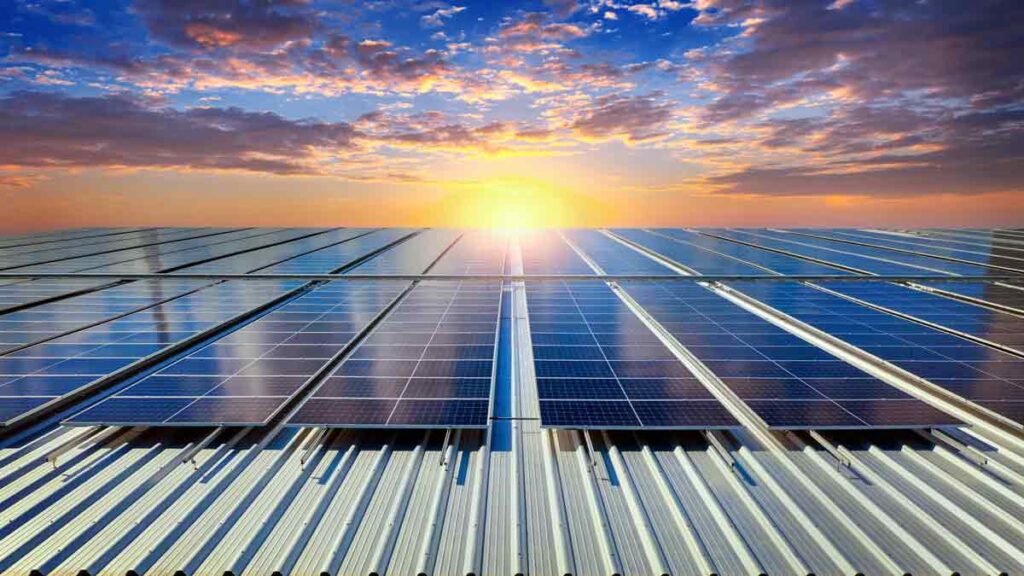

Overview of Solar Panels
1. Types of Solar Panels:
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels:
- Made from a single crystal structure.
- High efficiency and longevity.
- More expensive than other types.
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels:
- Made from multiple crystal structures.
- Slightly lower efficiency than monocrystalline.
- More affordable.
- Thin-Film Solar Panels:
- Made by depositing thin layers of photovoltaic material on a substrate.
- Flexible and lightweight.
- Lower efficiency and shorter lifespan compared to crystalline panels.
2. Components of a Solar Power System:
- Solar Panels: Convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Inverter: Converts DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity for home use.
- Mounting System: Secures the panels to the roof or ground.
- Battery Storage (optional): Stores excess energy for use when sunlight is not available.
- Charge Controller: Regulates the power going into and coming out of the battery storage.
Benefits of Solar Panels for Eco-Homes
- Renewable Energy Source:
- Provides a sustainable and inexhaustible energy supply.
- Reduces Electricity Bills:
- Lowers reliance on grid electricity, leading to significant cost savings over time.
- Environmental Impact:
- Produces clean energy, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and the home’s carbon footprint.
- Energy Independence:
- Offers greater self-sufficiency, especially in remote or off-grid locations.
- Increases Property Value:
- Homes equipped with renewable energy systems often have higher market value.
Considerations for Installing Solar Panels
- Sunlight Availability:
- Assess the average sunlight exposure in your area. Ideal locations have consistent and strong sunlight.
- Roof Suitability:
- Ensure the roof is suitable for installation in terms of space, orientation, and structural integrity.
- System Size:
- Determine the system size based on your energy consumption and available space.
- Budget:
- Consider the upfront costs of the system and potential savings over time.
- Incentives and Rebates:
- Research local, state, and federal incentives, rebates, and tax credits for solar installations.
Installation Process
- Site Assessment:
- Conduct a thorough analysis of sunlight exposure, roof condition, and potential shading.
- System Design:
- Create a system design based on energy needs, roof space, and budget.
- Permits and Approvals:
- Obtain necessary permits and approvals from local authorities.
- Installation:
- Install the solar panels, inverter, and other components.
- Connection to the Grid:
- Connect the system to the electrical grid or set up an off-grid system with battery storage.
- Inspection and Testing:
- Conduct final inspections and tests to ensure proper installation and operation.
Examples of Residential Solar Panels
- SunPower X-Series:
- High-efficiency monocrystalline panels.
- Excellent performance and durability.
- LG NeON R:
- High-efficiency monocrystalline panels.
- Strong performance and reliability.
- Canadian Solar HiKu:
- Cost-effective polycrystalline panels.
- Good efficiency and value for money.
Maintenance Tips
- Regular Cleaning: Remove dirt, dust, and debris from the panels to maintain efficiency.
- Inspect for Damage: Regularly check for any physical damage or wear on the panels and mounting system.
- Monitor Performance: Use the inverter and monitoring system to track energy production and address any issues promptly.
- Professional Maintenance: Schedule periodic professional inspections to ensure optimal performance.
Solar panels are a valuable addition to an eco-home, providing a reliable source of renewable energy and contributing to a more sustainable lifestyle. If you have any specific questions about solar panels or their integration into eco-homes, feel free to ask!